
PhD Course Requirements
The PhD degree requires approximately 30-40 hours of formal coursework with a grade of B- or better and a minimum GPA of 3.0. A PhD student must pass a written and oral Comprehensive Exam after the first year of study. Graduate work at this or other institutions, including courses taken for an MS degree, may be applied to the PhD coursework requirement at the discretion of the student's advisory committee and the University of Utah transfer credit policy. After completion of coursework, the student must pass a PhD written and oral Qualifying Examination. In addition to the coursework, 14 or more hours of research work hours (taken as BMI 7970) are required. This work must lead to completing and defending an original PhD dissertation demonstrating the student's capabilities to conceive and execute an independent research project.
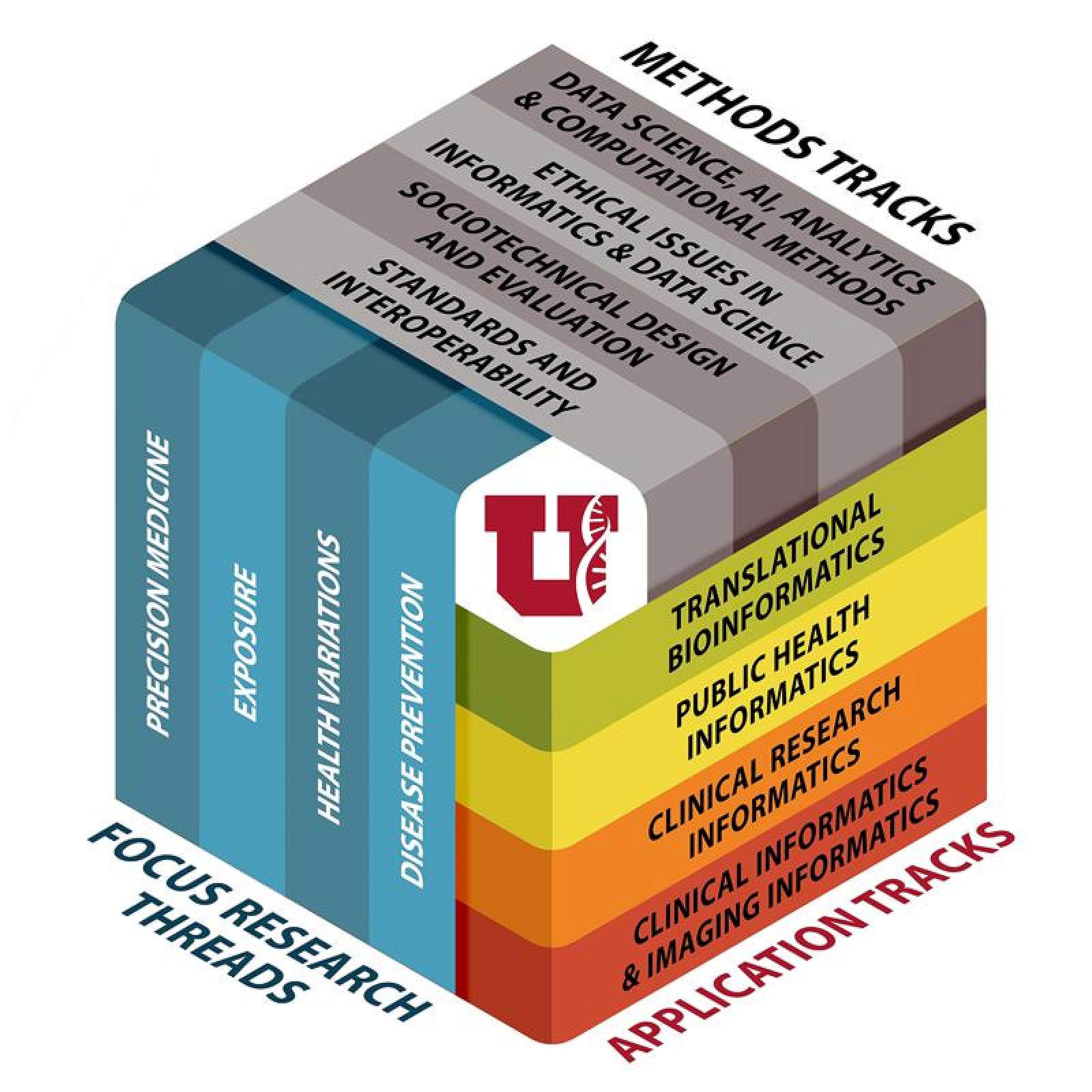
CURRICULUM CUBE
The strengths of our program faculty are utilized in the building of the curriculum. This figure shows the expertise by application area (green, yellow, orange, red), methodology (grey), and focal research area (teal). After a year of core courses, students join an application track and choose methods courses as needed. The research foci are woven through the curriculum and demonstrate departmental strengths, although students are not limited to these fields.
REQUIREMENTS
Typically 30-40 hours of formal class work (varies by dissertation topic and the advice of the student’s supervisory committee);
Successfully pass the comprehensive and qualifying exams;
A minimum of 14 hours dissertation research hours; and
A successfully defended dissertation.
REQUIRED COURSES
COURSE |
SEMESTER |
|
Prep Courses |
|
|
Intro to Programming |
1 |
|
Probability and Statistics for Biomedicine |
2 |
|
Foundational Courses |
|
|
Research Design * |
2 |
|
Terminologies and Standards * |
2 |
|
Grant Writing |
3 |
|
Application Area Courses |
|
|
Foundations of Bioinformatics * |
1 |
|
Public and Population Health Informatics * |
1 |
|
Foundations of Healthcare Informatics * |
1 |
|
Translational Informatics (CRI) |
3 |
|
Evaluation |
|
|
Comprehensive exam |
End of 2 |
|
Qualifying exam |
4 + |
ADDITIONAL COURSES
Ph.D. students must complete at least 21 additional credit hours after completion of core courses. This table shows the required and elective courses for the application domain tracks and the suggested courses for the methodology tracks. DBMI courses are annotated with an asterisk (*) – all others are external courses.
|
|
|||||||||||||
| COURSES | APPLICATIONS | METHODS | |||||||||||
| HC | CR | PH | TB | DA | SD | SI | |||||||
|
Foundational Courses (details in table above) |
R |
R |
R |
R |
|
|
|
||||||
|
Clinical Decision Support (BMI6300)* |
R |
|
E |
|
|
|
S |
||||||
|
Clinical Information Systems Architecture (BMI6440)* |
R |
R |
|
|
|
|
S |
||||||
|
Implementation of Systems in Healthcare settings (BMI6804)* |
R |
|
|
|
|
|
S |
||||||
|
Human System Interactions (BMI6821)* |
R |
|
E |
|
|
S |
|
||||||
|
Bioinformatics in Practice:RNA (BMI6019)* |
|
|
|
R |
|
|
|
||||||
|
Applied Computational Genomics (BMI6060)* |
|
|
|
R |
|
|
|
||||||
|
Applied Machine Learning (BMI6015)* |
|
|
|
|
S |
|
|
||||||
|
Deep Learning in Biomedicine (BMI6114)* |
|
|
|
|
S |
|
|
||||||
|
Clinical Database Design (BMI6203)* |
|
|
|
|
S |
S |
|
||||||
|
Biomedical Text Processing (BMI6115)* |
|
|
|
|
S |
|
|
||||||
|
Biomedical Data Wrangling (BMI 6016)* |
|
R |
E |
|
S |
|
S |
||||||
|
Terminologies and Standards (BMI 6120/5)* |
|
E |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
Data Mining (CS6140) |
|
E |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
Information Technology Security (IS6570) |
|
E |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
Data Warehouse Design and Implementation (IS6480) |
|
E |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
Database Systems (CS5530) |
|
E |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
Applied Informatics for Health Sci Research (NURS7104) |
|
E |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
Health Promotion and Social Determinants (NURS7420) |
E |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
Project Management in Health Informatics (NURS6661) |
E |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
Quality Improvement in Healthcare (NURS6772) |
E |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
Systems Analysis and Implementation (NURS6807) |
E |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
Genetics & Complex Disease (HGEN6421) |
|
|
|
E |
|
|
|
||||||
|
Signal Processing (BIOEN6670) |
|
|
|
E |
|
|
|
||||||
|
Introduction to Genetic Epidemiology (MDCRC 6000) |
|
|
|
E |
|
|
|
||||||
|
Genetics and Genomes (BIOL6420) |
|
|
|
E |
|
|
|
||||||
|
Introduction to Epidemiology (MDCRC6010) |
|
|
R |
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
Biomedical Big Data Science (PHS7020) |
|
E |
E |
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
Applied Modern Causal Inference (PHS7030) |
|
|
E |
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
Foundations of Population and Clinical Health (PHS7100) |
|
|
E |
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
Environmental Public Health (FPMD6700) |
|
|
E |
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
Intermediate Epidemiology (MDCRC6110) |
|
|
E |
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
GIS Environmental & Public Health (GEOG6190) |
|
|
E |
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
Data Mining (CS6140) |
|
E |
|
|
|
|
S |
||||||
|
Database Systems (CS5530) |
|
E |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
Introduction to Data Science, Artificial Intelligence (CS6300) |
|
|
|
|
S |
|
|
||||||
|
Visualization (CS6630) |
|
|
|
|
S |
|
|
||||||
|
Data Mining in Healthcare (IS6910) |
|
|
|
|
S |
|
S |
||||||
|
Advanced Data Mining (IS6483) |
|
|
|
|
S |
|
|
||||||
|
Information Extraction from Text (CS6390) |
|
|
|
|
S |
|
|
||||||
|
Learning Semantics for NLP (CS6936) |
|
|
|
|
S |
|
|
||||||
|
Artificial Intelligence (CS5300) |
|
|
|
|
S |
|
|
||||||
|
Statistical Inference (Math5080) |
|
|
|
|
S |
|
|
||||||
|
Human Computer Interaction (CS654) |
|
|
|
|
|
S |
|
||||||
|
Ergonomics (MEEN6100) |
|
|
|
|
|
S |
|
||||||
|
Human Factors Engineering (MEEN6120) |
|
|
|
|
|
S |
|
||||||
|
Advanced Human Cognition (PSY6120) |
|
|
|
|
|
S |
|
||||||
|
Brain, Cognition and Behavior (PSY6750) |
|
|
|
|
|
S |
|
||||||
|
Data Analysis and Decision Making (OIS6040) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
S |
||||||
|
Learning Semantics for NLP (CS6936) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
S |
||||||

